Understanding the Julian Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 and Beyond
Related Articles: Understanding the Julian Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 and Beyond
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Julian Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Julian Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 and Beyond
The Julian calendar, named after Julius Caesar, served as the standard calendar for much of the Western world for centuries. While it has been largely superseded by the Gregorian calendar, its historical significance and continued use in certain contexts make it a topic worthy of exploration. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Julian calendar, its historical background, its differences from the Gregorian calendar, and its continued relevance in the 21st century.
Historical Context and Origins:
The Julian calendar was introduced in 45 BC by Julius Caesar to rectify the inaccuracies of the existing Roman calendar, which was based on a lunar cycle and had become increasingly out of sync with the solar year. Caesar, advised by the Alexandrian astronomer Sosigenes, established a solar calendar with a year of 365 days, with an extra day added every four years, creating a leap year. This system aimed to align the calendar with the Earth’s revolution around the sun, ensuring the accurate marking of solstices and equinoxes.
The Julian Calendar’s Structure:
The Julian calendar comprises 12 months, with a total of 365 days. The order of months and their lengths largely resemble the modern Gregorian calendar:
- January: 31 days
- February: 28 days (29 days in leap years)
- March: 31 days
- April: 30 days
- May: 31 days
- June: 30 days
- July: 31 days
- August: 31 days
- September: 30 days
- October: 31 days
- November: 30 days
- December: 31 days
The Leap Year System:
The Julian calendar introduced the leap year system to account for the extra quarter of a day in the Earth’s revolution around the sun. Every four years, an extra day was added to February, making it 29 days long. This system aimed to maintain the calendar’s alignment with the solar year.
The Julian Calendar’s Inaccuracies:
While the Julian calendar was a significant improvement over its predecessors, it introduced its own inaccuracies. The Earth’s revolution around the sun takes approximately 365.2422 days, not 365.25 days as the Julian calendar assumed. This slight discrepancy of 11 minutes and 14 seconds led to a gradual drift of the calendar over time, causing the seasons to shift. By the 16th century, the Julian calendar was out of sync with the solar year by about 10 days.
The Gregorian Calendar’s Introduction:
To rectify the Julian calendar’s inaccuracies, Pope Gregory XIII introduced the Gregorian calendar in 1582. The Gregorian calendar adopted a more accurate leap year system, dropping three leap years every four centuries. This adjustment effectively stopped the calendar’s drift and ensured a closer alignment with the solar year.
The Julian Calendar’s Continued Relevance:
Despite its replacement by the Gregorian calendar, the Julian calendar remains relevant in several contexts:
- Religious Observances: Several Eastern Orthodox Churches and some other Christian denominations continue to follow the Julian calendar for religious purposes. This includes the calculation of Easter, which falls on a different date in the Julian calendar compared to the Gregorian calendar.
- Historical Research: The Julian calendar is crucial for historical research, as it was used for centuries and is embedded in many historical documents. Historians use it to accurately date events and understand the chronology of historical periods.
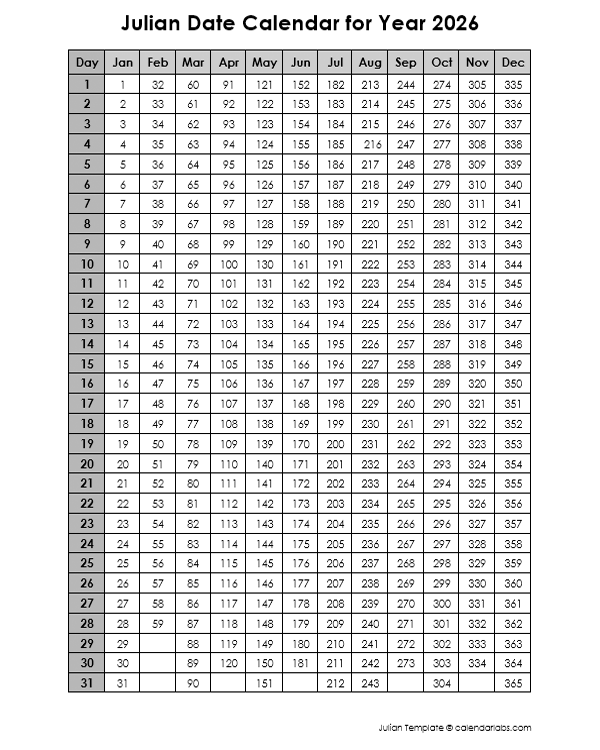
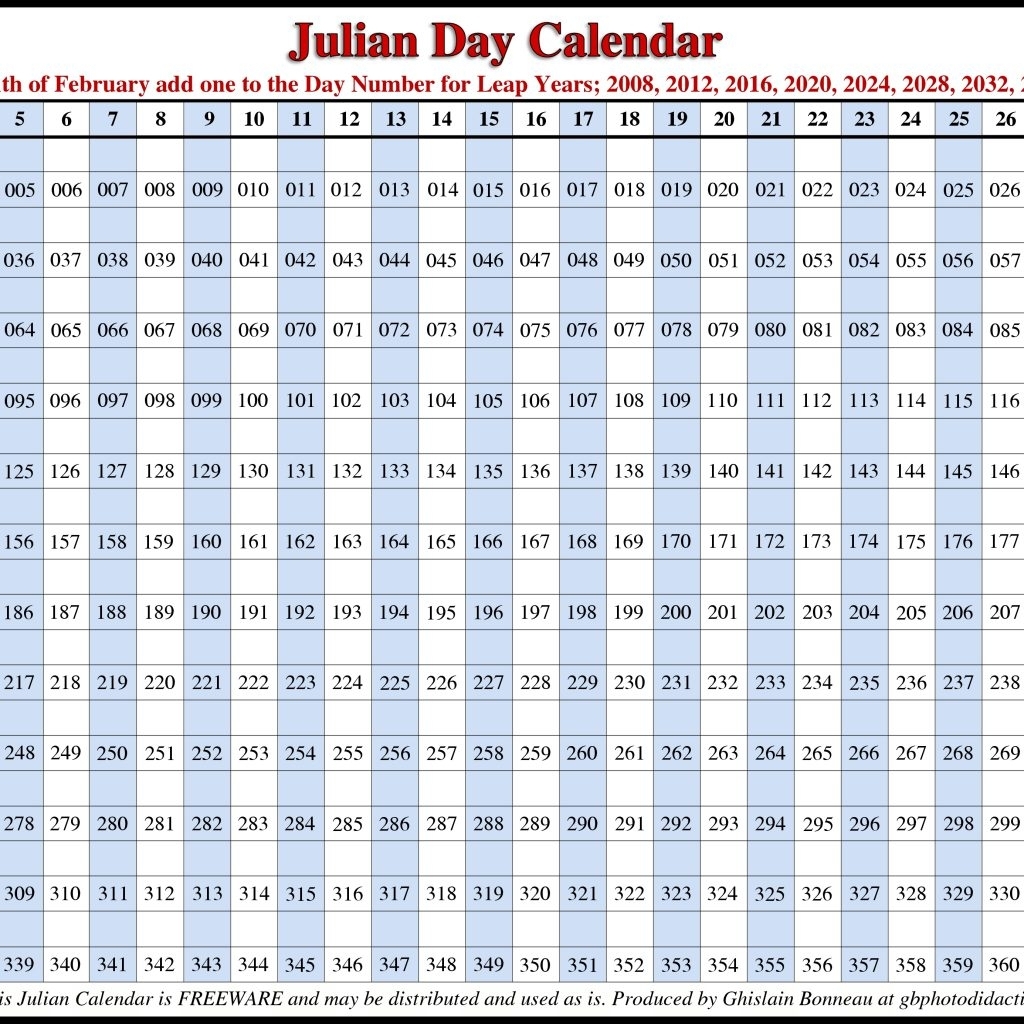
- Astronomy: The Julian calendar is still used in astronomy for specific calculations, such as the Julian date system, which provides a continuous count of days since a specific reference point.
Understanding the Julian Calendar in 2026:
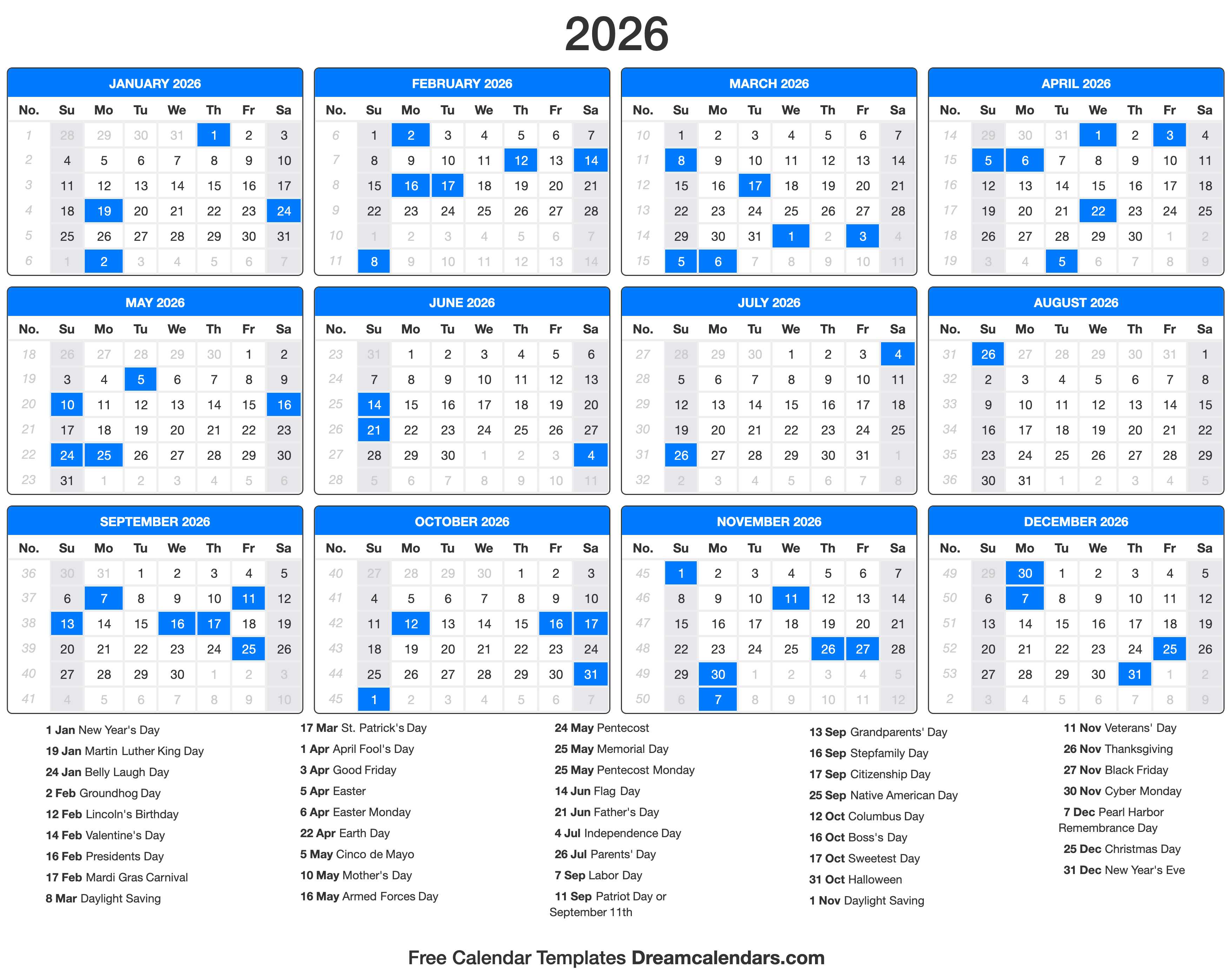
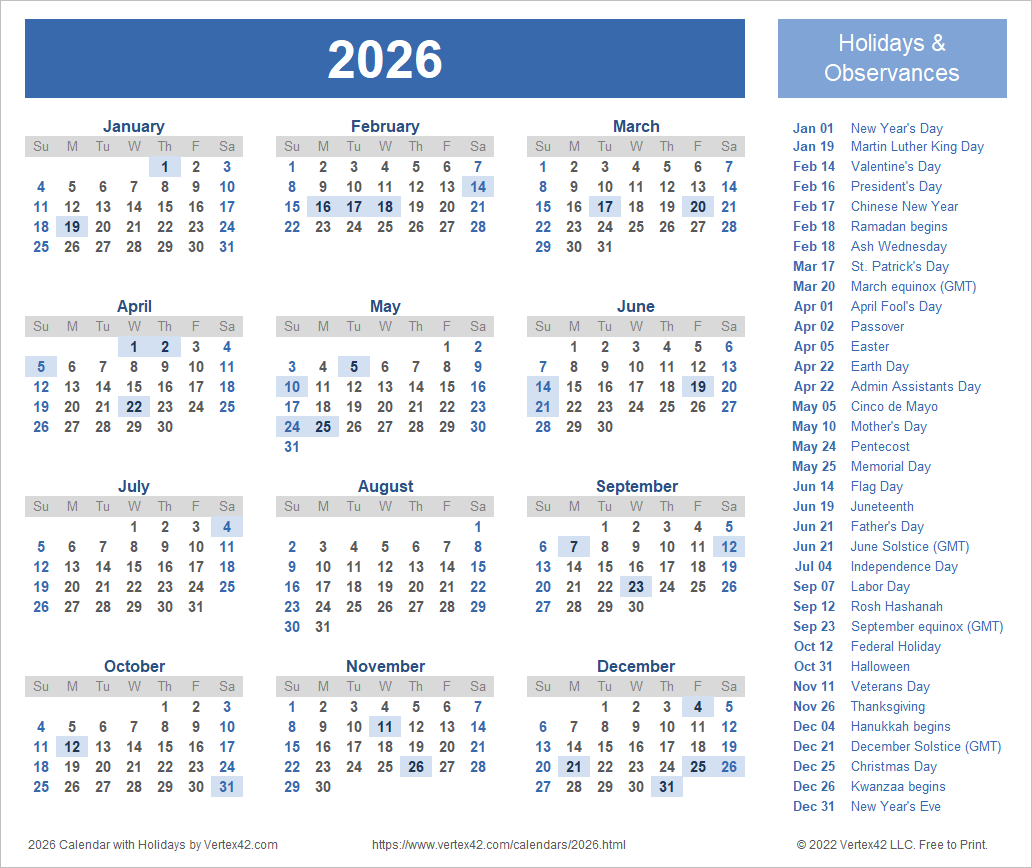
While the Julian calendar is not the primary calendar used in most of the world today, it is still relevant for understanding historical events and certain religious practices. In 2026, the Julian calendar will continue to be used by various groups, including:
- Eastern Orthodox Churches: They will celebrate Easter according to the Julian calendar, which will likely fall on a different date than the Gregorian calendar.
- Historical Researchers: Historians will continue to use the Julian calendar to understand and date events from the past.
- Astronomical Calculations: Astronomers may use the Julian date system for specific calculations.
FAQs about the Julian Calendar:
Q: What is the difference between the Julian and Gregorian calendars?
A: The main difference lies in the leap year system. The Julian calendar adds a leap year every four years, while the Gregorian calendar skips three leap years every four centuries. This difference leads to a gradual drift in the Julian calendar, causing it to be out of sync with the solar year.
Q: Why is the Julian calendar still used in some contexts?
A: The Julian calendar remains relevant for religious observances, historical research, and astronomical calculations.
Q: How do I convert dates from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar?
A: There are online conversion tools available that can help you convert dates between the Julian and Gregorian calendars. You can also find conversion tables in historical research resources.
Q: What are the benefits of using the Julian calendar?
A: The Julian calendar provides a historical context for understanding past events and is still used by some religious groups. It also has relevance in astronomical calculations.
Tips for Using the Julian Calendar:
- Be Aware of the Differences: When working with historical dates or religious observances, be mindful of the difference between the Julian and Gregorian calendars.
- Use Conversion Tools: Utilize online conversion tools or tables to accurately convert dates between the two calendars.
- Contextualize Historical Events: Understand the calendar system used in historical documents to accurately interpret events.
Conclusion:
The Julian calendar, despite its historical significance and continued use in specific contexts, has been largely replaced by the more accurate Gregorian calendar. However, understanding its history, structure, and relevance remains crucial for appreciating the evolution of timekeeping and its impact on various aspects of our world. By recognizing the Julian calendar’s role in history and its continued use in certain communities, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between calendars, time, and human civilization.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Julian Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 and Beyond. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!